How to Design an Agenttic AI Architecture with LangGraph and OpenAI Using Adaptive Deliberation, Memory Graph, and Reflection Loops
In this tutorial, we build a truly advanced Agentic AI system using LangGraph and OpenAI models by bypassing simple scheduler, executor loops. We use dynamic speech, where the agent decides between quick and deep thinking; a Zettelkasten-style memory graph that stores atomic information and automatically links to related ones; and a controlled tooling approach that enforces constraints during execution. By combining systematic state management, memory-aware retrieval, logical learning, and the invocation of controlled tools, we show that modern systems can think, act, learn, and evolve rather than reacting in a single pass. Check it out FULL CODES here.
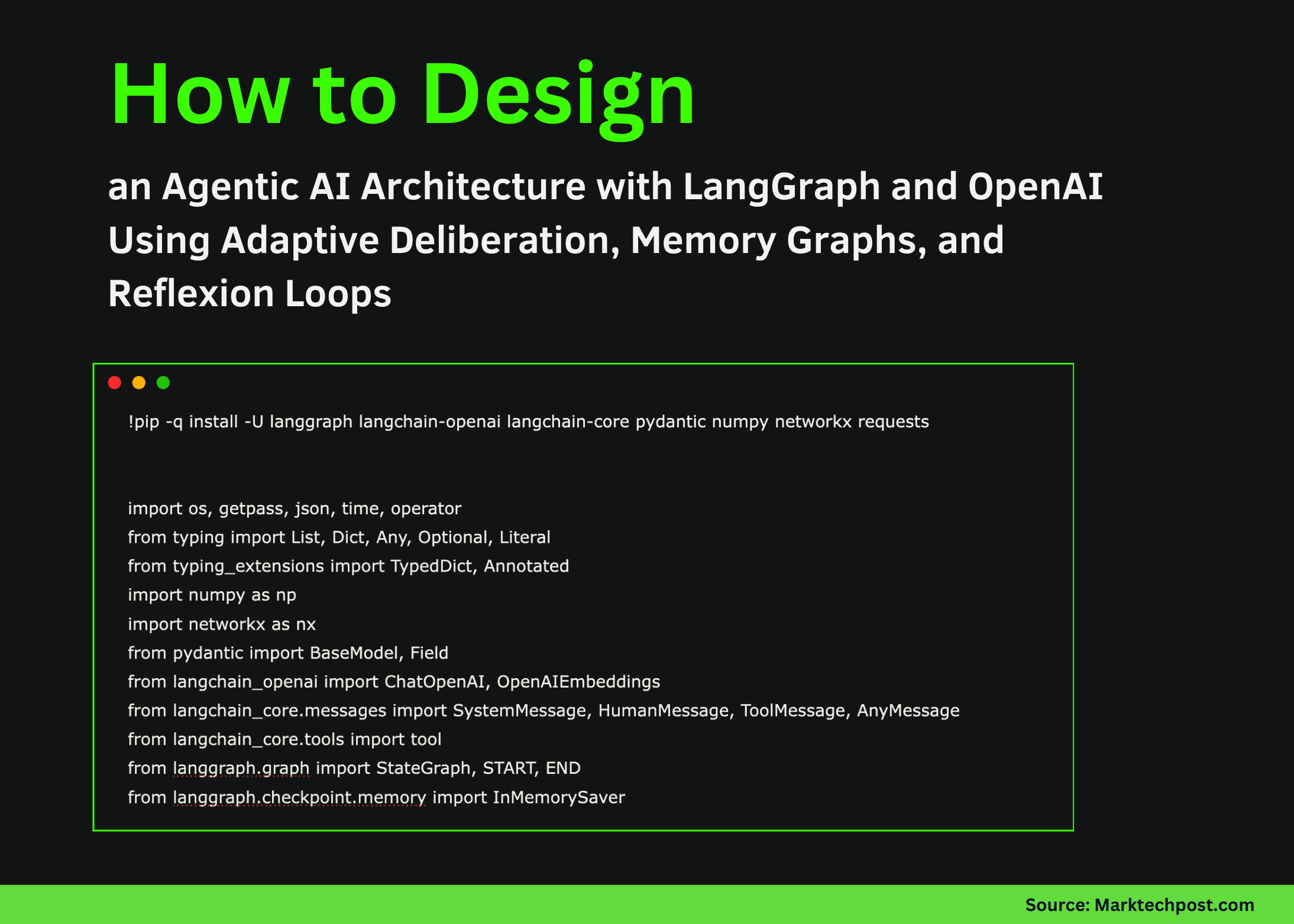
!pip -q install -U langgraph langchain-openai langchain-core pydantic numpy networkx requests
import os, getpass, json, time, operator
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Optional, Literal
from typing_extensions import TypedDict, Annotated
import numpy as np
import networkx as nx
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage, HumanMessage, ToolMessage, AnyMessage
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaverSet up the workspace by installing all the required libraries and importing the necessary modules. We include LangGraph for instrumental music, LangChain for abstract models and tools, and libraries that support memory graphs and numerical operations. Check it out FULL CODES here.
if not os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY"):
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Enter OPENAI_API_KEY: ")
MODEL = os.environ.get("OPENAI_MODEL", "gpt-4o-mini")
EMB_MODEL = os.environ.get("OPENAI_EMBED_MODEL", "text-embedding-3-small")
llm_fast = ChatOpenAI(model=MODEL, temperature=0)
llm_deep = ChatOpenAI(model=MODEL, temperature=0)
llm_reflect = ChatOpenAI(model=MODEL, temperature=0)
emb = OpenAIEmbeddings(model=EMB_MODEL)We securely load the OpenAI API key at runtime and implement language models used for fast, deep, and intuitive reasoning. We also develop an embedding model that enables semantic similarity in memory. This separation allows us to easily change the depth of thought while maintaining the allocated space for the memory representation. Check it out FULL CODES here.
class Note(BaseModel):
note_id: str
title: str
content: str
tags: List[str] = Field(default_factory=list)
created_at_unix: float
context: Dict[str, Any] = Field(default_factory=dict)
class MemoryGraph:
def __init__(self):
self.g = nx.Graph()
self.note_vectors = {}
def _cos(self, a, b):
return float(np.dot(a, b) / ((np.linalg.norm(a) + 1e-9) * (np.linalg.norm(b) + 1e-9)))
def add_note(self, note, vec):
self.g.add_node(note.note_id, **note.model_dump())
self.note_vectors[note.note_id] = vec
def topk_related(self, vec, k=5):
scored = [(nid, self._cos(vec, v)) for nid, v in self.note_vectors.items()]
scored.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return [{"note_id": n, "score": s, "title": self.g.nodes[n]["title"]} for n, s in scored[:k]]
def link_note(self, a, b, w, r):
if a != b:
self.g.add_edge(a, b, weight=w, reason=r)
def evolve_links(self, nid, vec):
for r in self.topk_related(vec, 8):
if r["score"] >= 0.78:
self.link_note(nid, r["note_id"], r["score"], "evolve")
MEM = MemoryGraph()We build an agent memory graph inspired by the Zettelkasten method, where each interaction is stored as an atomic note. We embed each note and connect it to related notes using matching points. Check it out FULL CODES here.
@tool
def web_get(url: str) -> str:
import urllib.request
with urllib.request.urlopen(url, timeout=15) as r:
return r.read(25000).decode("utf-8", errors="ignore")
@tool
def memory_search(query: str, k: int = 5) -> str:
qv = np.array(emb.embed_query(query))
hits = MEM.topk_related(qv, k)
return json.dumps(hits, ensure_ascii=False)
@tool
def memory_neighbors(note_id: str) -> str:
if note_id not in MEM.g:
return "[]"
return json.dumps([
{"note_id": n, "weight": MEM.g[note_id][n]["weight"]}
for n in MEM.g.neighbors(note_id)
])
TOOLS = [web_get, memory_search, memory_neighbors]
TOOLS_BY_NAME = {t.name: t for t in TOOLS}We describe external tools that an agent can invoke, including web access and memory-based retrieval. We integrate these tools in a systematic way so that the agent can query the past or retrieve new information when needed. Check it out FULL CODES here.
class DeliberationDecision(BaseModel):
mode: Literal["fast", "deep"]
reason: str
suggested_steps: List[str]
class RunSpec(BaseModel):
goal: str
constraints: List[str]
deliverable_format: str
must_use_memory: bool
max_tool_calls: int
class Reflection(BaseModel):
note_title: str
note_tags: List[str]
new_rules: List[str]
what_worked: List[str]
what_failed: List[str]
class AgentState(TypedDict, total=False):
run_spec: Dict[str, Any]
messages: Annotated[List[AnyMessage], operator.add]
decision: Dict[str, Any]
final: str
budget_calls_remaining: int
tool_calls_used: int
max_tool_calls: int
last_note_id: str
DECIDER_SYS = "Decide fast vs deep."
AGENT_FAST = "Operate fast."
AGENT_DEEP = "Operate deep."
REFLECT_SYS = "Reflect and store learnings."We formalize the agent’s internal representations using structured schemas for discussion, action objectives, visualization, and worldview. We also describe system commands that direct behavior in fast and deep modes. This ensures that the agent’s reasoning and decisions remain consistent, interpretable, and controllable. Check it out FULL CODES here.
def deliberate(st):
spec = RunSpec.model_validate(st["run_spec"])
d = llm_fast.with_structured_output(DeliberationDecision).invoke([
SystemMessage(content=DECIDER_SYS),
HumanMessage(content=json.dumps(spec.model_dump()))
])
return {"decision": d.model_dump(), "budget_calls_remaining": st["budget_calls_remaining"] - 1}
def agent(st):
spec = RunSpec.model_validate(st["run_spec"])
d = DeliberationDecision.model_validate(st["decision"])
llm = llm_deep if d.mode == "deep" else llm_fast
sys = AGENT_DEEP if d.mode == "deep" else AGENT_FAST
out = llm.bind_tools(TOOLS).invoke([
SystemMessage(content=sys),
*st.get("messages", []),
HumanMessage(content=json.dumps(spec.model_dump()))
])
return {"messages": [out], "budget_calls_remaining": st["budget_calls_remaining"] - 1}
def route(st):
return "tools" if st["messages"][-1].tool_calls else "finalize"
def tools_node(st):
msgs = []
used = st.get("tool_calls_used", 0)
for c in st["messages"][-1].tool_calls:
obs = TOOLS_BY_NAME[c["name"]].invoke(c["args"])
msgs.append(ToolMessage(content=str(obs), tool_call_id=c["id"]))
used += 1
return {"messages": msgs, "tool_calls_used": used}
def finalize(st):
out = llm_deep.invoke(st["messages"] + [HumanMessage(content="Return final output")])
return {"final": out.content}
def reflect(st):
r = llm_reflect.with_structured_output(Reflection).invoke([
SystemMessage(content=REFLECT_SYS),
HumanMessage(content=st["final"])
])
note = Note(
note_id=str(time.time()),
title=r.note_title,
content=st["final"],
tags=r.note_tags,
created_at_unix=time.time()
)
vec = np.array(emb.embed_query(note.title + note.content))
MEM.add_note(note, vec)
MEM.evolve_links(note.note_id, vec)
return {"last_note_id": note.note_id}We use the main agent behaviors as LangGraph nodes, including chat, action, tool use, completion, and reflection. We plan how information flows between these stages and how decisions affect action. Check it out FULL CODES here.
g = StateGraph(AgentState)
g.add_node("deliberate", deliberate)
g.add_node("agent", agent)
g.add_node("tools", tools_node)
g.add_node("finalize", finalize)
g.add_node("reflect", reflect)
g.add_edge(START, "deliberate")
g.add_edge("deliberate", "agent")
g.add_conditional_edges("agent", route, ["tools", "finalize"])
g.add_edge("tools", "agent")
g.add_edge("finalize", "reflect")
g.add_edge("reflect", END)
graph = g.compile(checkpointer=InMemorySaver())
def run_agent(goal, constraints=None, thread_id="demo"):
if constraints is None:
constraints = []
spec = RunSpec(
goal=goal,
constraints=constraints,
deliverable_format="markdown",
must_use_memory=True,
max_tool_calls=6
).model_dump()
return graph.invoke({
"run_spec": spec,
"messages": [],
"budget_calls_remaining": 10,
"tool_calls_used": 0,
"max_tool_calls": 6
}, config={"configurable": {"thread_id": thread_id}})We integrate all the nodes in the LangGraph workflow and integrate it with the specified state management. We also define a reusable runner function that executes the agent while saving memory across runs.
In conclusion, we have shown how an agent can continuously improve its behavior through reflection and memory rather than relying on static information or hard-coded cognition. We used LangGraph to organize discussion, execution, tool management, and reflection as a parallel graph, while OpenAI models provide inference and synthesis capabilities for each category. This approach showed how agent AI systems can approach self-governance by leveraging their deep thinking, reusing prior knowledge, and encoding lessons as persistent memory, creating a viable foundation for building powerful, self-improving agents in real-world applications.
Check it out FULL CODES here. Also, feel free to follow us Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to Our newspaper. Wait! are you on telegram? now you can join us on telegram too.
Check out our latest issue of ai2025.deva 2025-focused analytics platform that transforms model implementations, benchmarks, and ecosystem activity into structured datasets that you can sort, compare, and export
Asif Razzaq is the CEO of Marktechpost Media Inc. As a visionary entrepreneur and engineer, Asif is committed to harnessing the power of Artificial Intelligence for the benefit of society. His latest endeavor is the launch of Artificial Intelligence Media Platform, Marktechpost, which stands out for its extensive coverage of machine learning and deep learning stories that sound technically sound and easily understood by a wide audience. The platform boasts of more than 2 million monthly views, which shows its popularity among viewers.